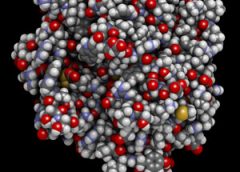
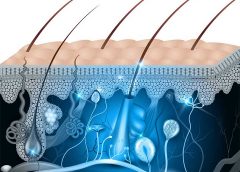
Jitka Petrlova at Lund University, Sweden, together with Peter Bond’s team at the A*STAR Bioinformatics Institute, has discovered a strategy that the body uses to neutralize invading microbes. This finding is a critical development in fighting bacteria in skin wounds. Read more.
Read MoreSearch Results for: skin
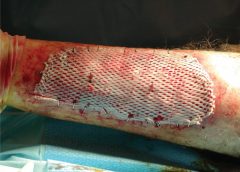
Skin Damage Associated with Moisture and Pressure
Skin damage associated with moisture and pressure
Program Objectives
- Identify how wounds are classified according to wound depth and etiology.
- Describe the etiology of a pressure injury (PI) and incontinence-associated skin damage (IAD).
- Discuss evidence-based protocols of care of prevention and management if IAD and PIs.
- Describe the NPUAP-EPUAP Pressure Injury Classification System.
- Identify appropriate products that can be used for preventioin and treatment of IAD and PIs.
Our Speakers
 |
 |
Submit below to view the Webinar and download Slidedeck
*By downloading this (product) you are opting in to receiving information from Healthcom Media and Affiliates. Or the details, including your email address/mobile number, may be used to keep you informed about future products and services.
Read MoreWinning the battle of skin tears in an aging population
ON DEMAND webinar
Winning the battle of skin tears in an aging population
This April 25th, 2017 webinar overviews a significant challenge that healthcare providers encounter daily.
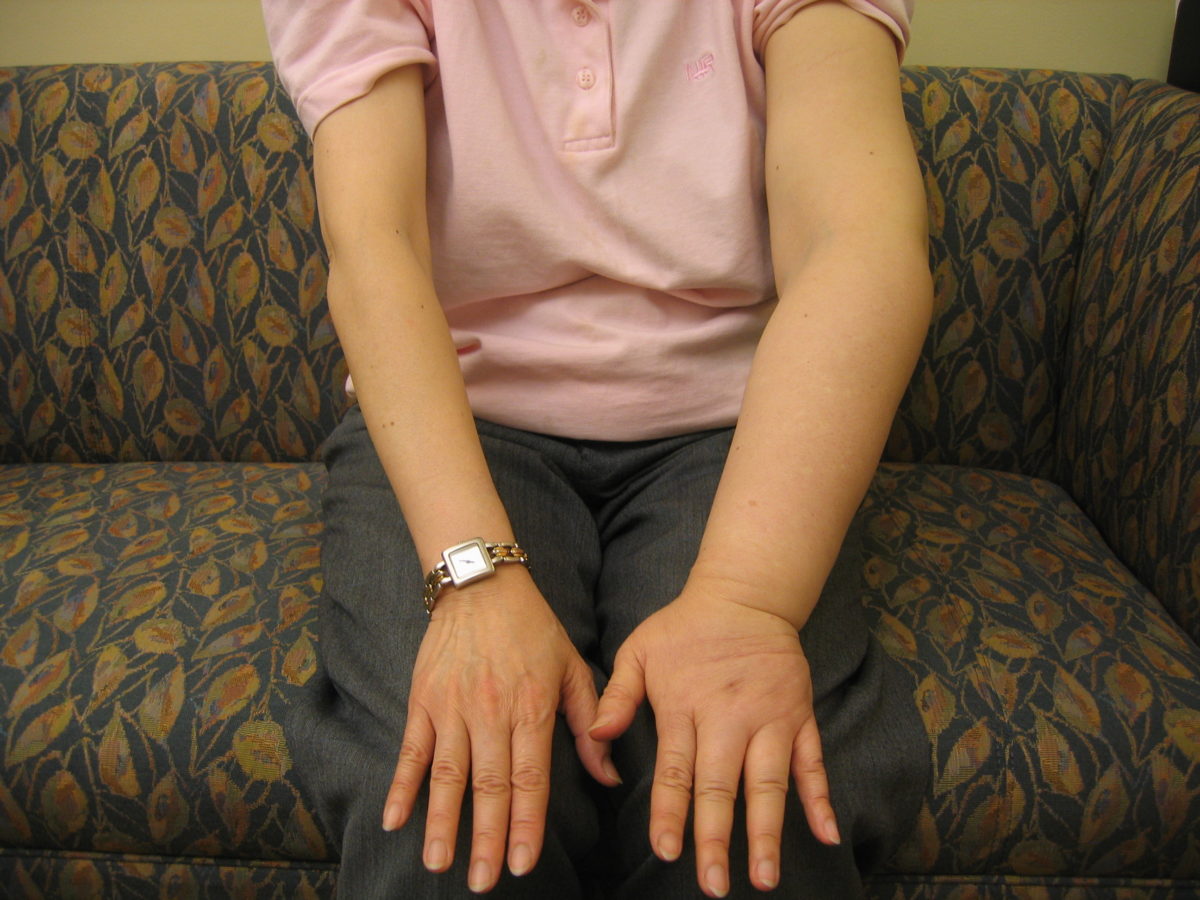
“Skin tears” may sound like a relatively minor event, but in reality, these injuries can have a significant impact on the quality of patients’ lives in the form of pain, infection, and limited mobility. The incidence of skin tears has been reported to be as high as 1.5 million annually, and with an aging population, this number is likely to go higher. In this webinar, experts will explain how nurses can use an evidence-based approach—including following practice guidelines to assess the wound and select the proper dressing—for managing skin tears and minimizing their negative effects.
Our Speakers
The skin tear challenge

Kimberly LeBlanc
MN, RN, CETN(C)
Advanced practice nurse, KDS Professional Consulting President, International Skin Tear Advisory Panel
An expert in skin tears, Kimberly will briefly set the stage by addressing the seriousness of skin tears and briefly addressing assessment such as classification.
The main focus will be on management, including goals of care, wound cleaning, wound bed preparation, and dressing selection.
Content will include information from the 2016 consensus statement on skin tears published in Advances in Skin & Wound Care.
|
Tips and techniques for managing dressings for skin tears

Shannon Cyphers
RN, BSN, WCC
Clinical Account Manager, ConvaTec, Inc.
Shannon will present wound and skin care product applications to help manage skin tears.
|
Submit below to view the Webinar and download Slidedeck
Questions or comments? Please contact [email protected]
*By downloading this (product) you are opting in to receiving information from Healthcom Media and Affiliates. Or the details, including your email address/mobile number, may be used to keep you informed about future products and services.
Read MoreSkin Damage Associated with Moisture and Pressure ebook

> Fill out this form to receive your free ebook
|sponsored by Convatec|
by downloading this ebook you are opting in to receiving information from Convatec.
Read MoreBetter Skin Grafts – take only one layer
Research shows that a skin-graft harvesting system aids chronic wound recovery and reduces care costs by accelerating the healing process.
More than six million cases of chronic wounds cost $20 billion each year in the United States. Diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, surgical site wounds, and traumatic injuries to high-risk patients account for most wounds that won’t heal. (more…)
Read MoreNew Approach to Wound Healing Easy on Skin, Tough on Bacteria
Washington, D.C. — In a presentation to the American Chemical Society meeting, Ankit Agarwal, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, described an experimental approach to wound healing that could take advantage of silver’s anti-bacterial properties, while sidestepping the damage silver can cause to cells needed for healing.
Silver is widely used to prevent bacterial contamination in wound dressings, says Agarwal, “but these dressings deliver a very large load of silver, and that can kill a lot of cells in the wound.” (more…)
Read MoreTheraSkin® – New V.A. Contract
NEWPORT NEWS, Va., July 18, 2017 /PRNewswire/ — All four sizes of TheraSkin® are now available to nearly 9 million veterans treated by more than 110 VA Medical Centers and 800 Community Based Outpatient Centers (CBOCs) nationwide as a result of the Department of Veterans Affairs updating their Federal Supply Schedule. (more…)
Read MoreFish Skin for Human Wounds: Iceland’s Pioneering Treatment
The FDA-approved skin substitute reduces inflammation and transforms chronic wounds into acute injuries.
Six hours north of Reykjavik, along a narrow road tracing windswept fjords, is the Icelandic town of Isafjordur, home of 3,000 people and the midnight sun. On a blustery May afternoon, snow still fills the couloirs that loom over the docks, where the Pall Palsson, a 583-ton trawler, has just returned from a three-day trip. Below the rust-spotted deck, neat boxes are packed with freshly caught fish and ice. “If you take all the skins from that trawler,” says Fertram Sigurjonsson, the chairman and chief executive officer of Kerecis Ltd., gesturing over the catch, “we would be able to treat one in five wounds in the world.” (more…)
Read MoreSevere Burn Victims May Soon Be Able to Regrow Hair-Bearing Skin
PolarityTE (TM) Regenerates Full-Thickness Hair-Bearing Skin in Burns and Wounds Using Their Revolutionary Platform Technology. First ever known successful regeneration of full-thickness skin and hair; Company poised to initiate human trial in the third quarter of 2017; Management to host conference call Thursday, June 8th at 4:30pm ET.
Salt Lake City, UT — (Marketwired) — 06/08/17 — PolarityTE™, Inc. (NASDAQ: COOL) today announced pre-clinical results demonstrating that the Company’s lead product, SkinTE™, regenerated full-thickness, organized skin and hair follicles in third degree burn wounds. The findings represent the first known successful regeneration of skin and hair in full-thickness swine wound models, the standard animal model for human skin. The Company expects to initiate a human clinical trial evaluating the autologous homologous SkinTE™ construct in the third quarter of 2017. (more…)
Read MoreSkin Care & Treatment

Long-Term Outcome of Pediatric Traumatic Wound Repair: Suture Versus Tissue Adhesive

Breaking silos: Effective wound healing means treatment across the continuum
NYU docs use machine learning

One Doctor Exploring Wound Care on Earth and in Space
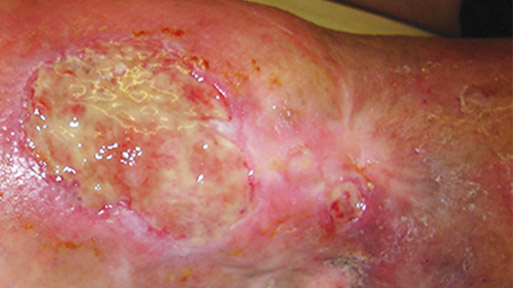
Management of Patients With Venous Leg Ulcers
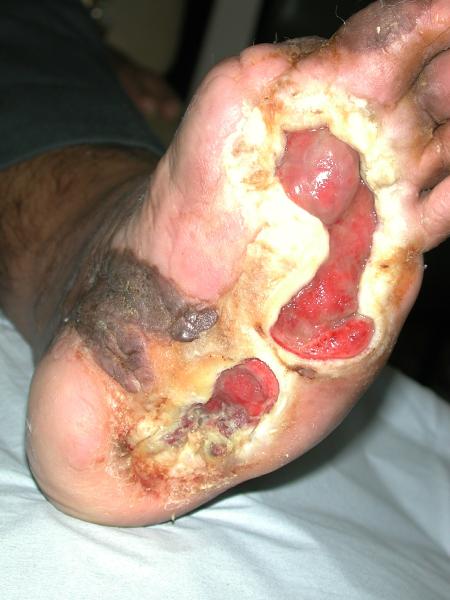
Reduction of 50% in Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Stem Cells
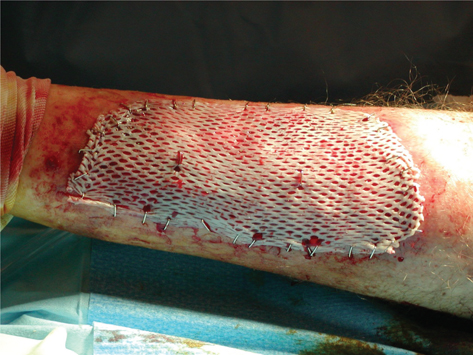
Better Skin Grafts – take only one layer

Skin substitutes: Understanding product differences

Frequently asked questions about support surfaces
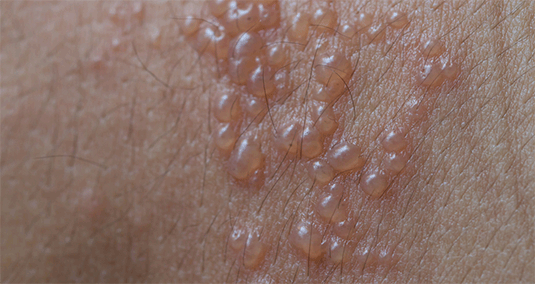
Herpes zoster: Understanding the disease, its treatment, and prevention

Lymphedema and lipedema: What every wound care clinician should know

Clinician Resources
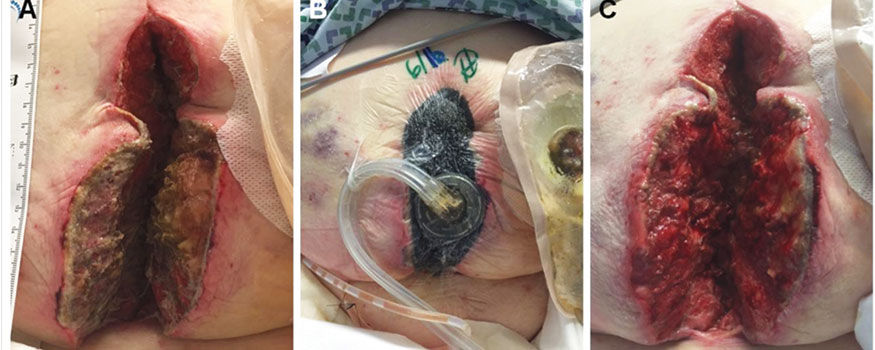
Instill instead: Negative pressure wound therapy with instillation for complex wounds

Doing it cheaply vs. doing what’s best for patients
Clinical Notes: biofilm, bariatric surgery, statins and more

Wise use of antibiotics in patients with wound infections
Causes, prevention, and treatment of epibole

Clinical Notes: Moldable Skin Barrier, hypoglycemia, diabetic food ulcers

Clinician Resources: human trafficking, npuap, caregiver, ostomy, HIV

How to apply silver nitrate
No more skin tears
Clinical Notes: ostomy, pressure ulcer, burn treatment

Buzz Report: Latest trends, Part 1

Don’t go it alone

Clincal Notes: Analysis, Osteomyelitis, sickle cell, maggot

Restorative nursing programs help prevent pressure ulcers
Clinician Resources: Ulcer Prevention, CAUTI, Negative Bacteria
Clinician Resources: NPUAP, Pressure Ulcer Treatment, NIOSH
Providing evidence-based care for patients with lower-extremity cellulitis

Ankle-brachial index: A dirty word?
Palliative wound care: Part 2
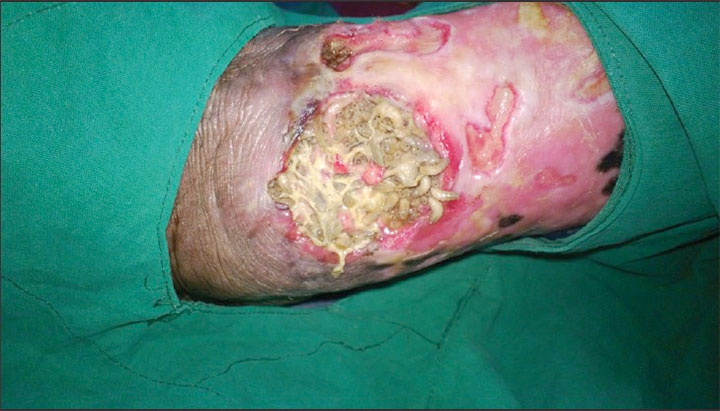
Using maggots in wound care: Part 2
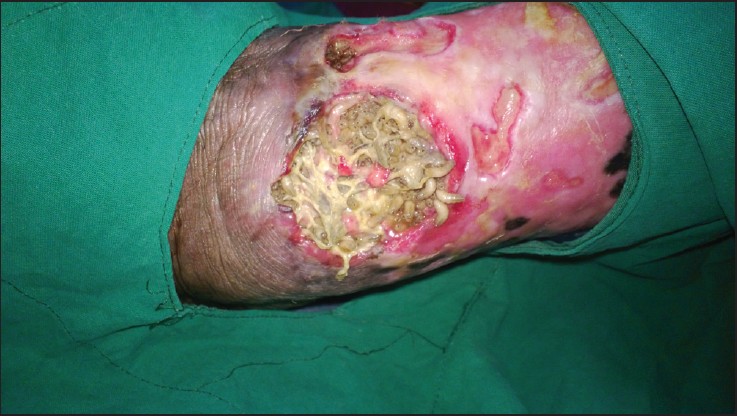
Using maggots in wound care: Part 1
Clinician Resources: Patient Safety, Ostomy, Wound Management
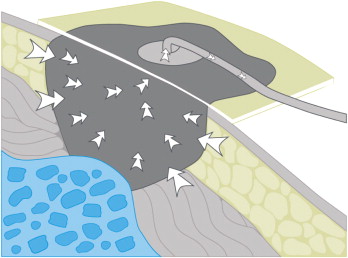
Guidelines for safe negative-pressure wound therapy

Clinician Resources: Intl Ostomy Assoc., Substance Use Disorder
“This is how we’ve always done it” isn’t good enough
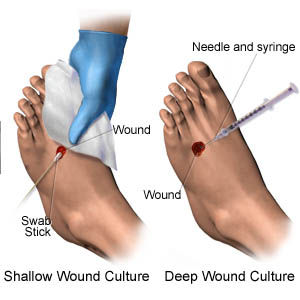
When and how to culture a chronic wound
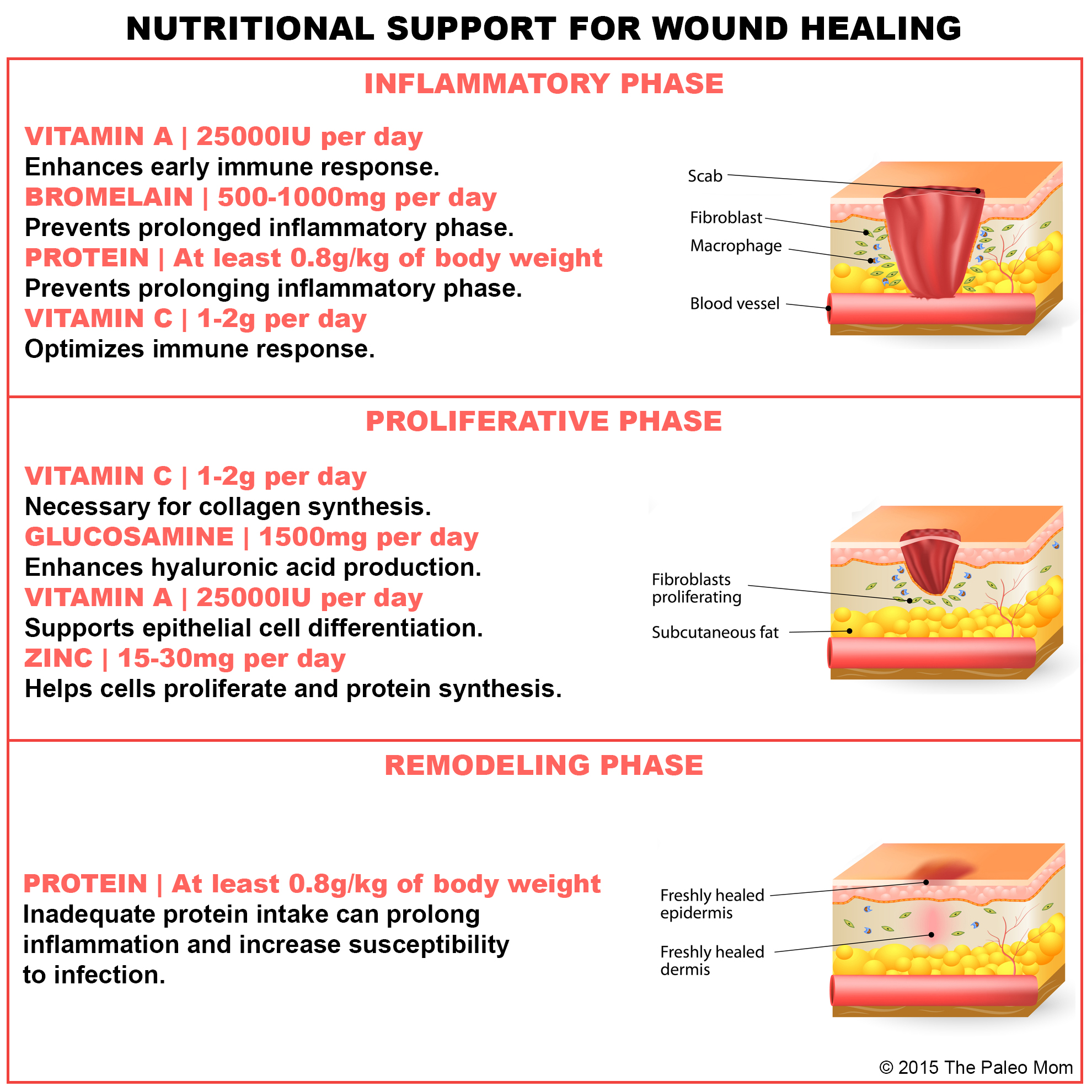
How dietary protein intake promotes wound healing
From the Editor – Wound care superhero
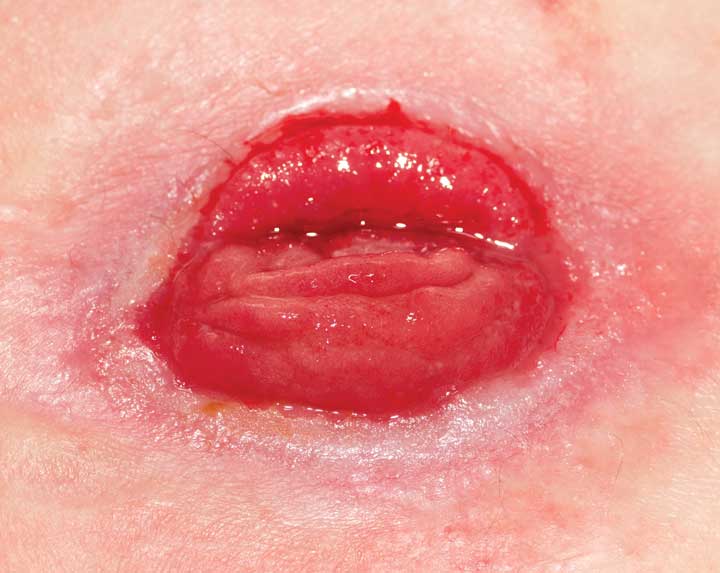
Understanding stoma complications
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers
Lymphedema 101 – Part 2: Treatment
Ask the treatment expert: Should treatment nurses be certified?
Discovery Promises Unique Medicine for Treatment of Chronic and Diabetic Wounds
Better Skin Grafts – take only one layer
Research shows that a skin-graft harvesting system aids chronic wound recovery and reduces care costs by accelerating the healing process.
More than six million cases of chronic wounds cost $20 billion each year in the United States. Diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, surgical site wounds, and traumatic injuries to high-risk patients account for most wounds that won’t heal. (more…)
Read MoreSkin substitutes: Understanding product differences
Skin substitutes (also called tissuebased products and dermal replacements) are a boon to chronic wound management when traditional therapies have failed. When selecting skin substitutes for their formularies, wound care professionals have many product options—and many decisions to make.
Repair of skin defects has been a pressing concern for centuries. As early as the 15th century BC, Egyptian physicians chronicled procedures and herbal treatments to heal wounds, including xenografts (skin from another species). The practice of applying allografts (human cadaver skin) to wounds was first documented in 1503. In 1871, autologous skin grafting (skin harvested from the the person with the wound) was tried. Next came epithelial- cell seeding, which involves scraping off the superficial epithelium of healthy skin and transplanting the cells onto the wound. (more…)
Read More