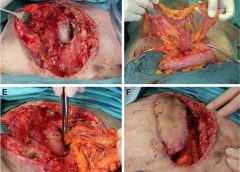
Introduction: Deep sternal wound infections (DSWIs) are rare but devastating complication after median sternotomy following cardiac surgery. Especially in the presence of artificial material or inadequate preliminary muscle flaps, the pedicled omentum flap is due to its immunological properties, the predetermined flap in salvage procedures. (more…)
Read MoreMonth: August 2017
Slugs inspire a surgical bio glue
Slugs secrete biological defensive mucus that has now inspired a new type of surgical glue, prepared by researchers. This “bio-glue” has three main properties, it can move with the body, it is incredibly strong and it can stick to wet surfaces. The results of this breakthrough are published this week in the journal Science. (more…)
Read MoreCould probiotics replace antibiotics in wound healing?
The microbiome is known to play a major role in gut health, but what about our skin? Billions of bacteria reside there, and the probiotic types may hold great potential to prevent infections during wound healing.
Our skin provides a natural barrier to the environment. This is crucial for our health, as skin protects us from invasive pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. (more…)
Read MoreStudy shows link between prophylactic dressing use and reduction in pressure injury rates
A new study shows a clear association between the prophylactic use of five-layer foam sacral dressings and reductions in pressure injury rates. Specifically, the study looked at the prophylactic use of Mölnlycke’s Mepilex® Border Sacrum dressing in the acute care setting over a six-year period (2010-2015). (more…)
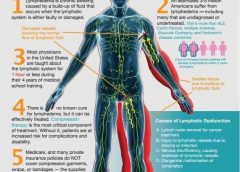
Read MoreHope for first drug against lymphedema
Many cancer patients, especially those who’ve undergone breast cancer treatment, experience painful, swollen limbs, a condition called lymphedema.
Now researchers say they’ve found an underlying mechanism that could eventually lead to the first drug therapy for the debilitating condition. (more…)
Read MoreCervical Biopsy more efficient, less painful via new method
Physicians evaluate new device to test for cervical cancer. Comparison of Tissue Yield Using Frictional Fabric Brush Versus Sharp Curettage For Endocervical Curettage.
Women undergoing cervical biopsies might have lower odds of repeat tests with a rotating fabric brush than a sharp instrument because the soft device may capture more cells for analysis, a recent study suggests. Furthermore, biopsies with the softer tool may be less painful, researchers say. Cervical biopsies sometimes fail to collect enough cells from the cervix to accurately test for cancer, in which case another biopsy is needed. (more…)
Read MoreScientists Seek People with Primary Progressive MS and Other Forms of MS to Study Gut Bacteria
Investigators at the University of California in San Francisco are recruiting people with MS for an international study of the gut microbiome – the population of bacteria in the gut – in MS. They are seeking people with primary progressive MS nationwide (there is no need for onsite visits), as well as people with any other type of MS who can make a one-time visit to San Francisco, New York, Boston or Pittsburgh. The overall purpose of these studies is to investigate the potential role of gut bacteria in MS.
Scientists Focus on Gut Flora for Future Treatments of Autoimmune Diseases
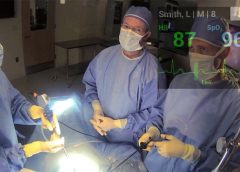
Read MoreNurses, Doctors and Hospitals use Google Glass
For surgical collaboration; rural telemedicine, nurses and doctors at Hospitals use Google Glass. Indianapolis-based Hodei Technology is bringing Glass to hospitals in two different ways: as a tool for surgeons to teach, communicate, and collaborate (via a product called Ikasi) and, via a product called Gemini, as a new kind of telemedicine, which CEO Guy Mascaro describes as “first person point-of-view telepresence”.
A lot of people think Google Glass, the tech company’s experiment with augmented reality and wearable computing, died when the Glass Explorer program closed up shop in 2015. In fact, the technology has continued to find a home with enterprise applications, particularly in healthcare. (more…)
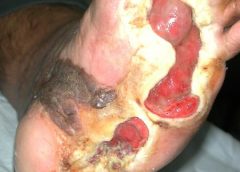
Read MoreGene Therapy for Non-Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Starts Phase III Trial
Safety and Efficacy Study of VM202 in the Treatment of Chronic Non-Healing Foot Ulcers. This study will assess the safety and efficacy of using gene therapy via intramuscular injections of the calf for patients with chronic non-healing foot ulcers.
The first patient has been dosed in a Phase III trial assessing ViroMed’s VM202, the first pivotal study of a gene therapy indicated for patients with nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers (NHU) and concomitant peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The Phase III trial (NCT02563522) is a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study designed to evaluate VM202 for safety and efficacy in 300 adults with a diabetic foot ulcer and concomitant PAD. Two hundred patients will be randomized to VM202 and the other 100 to placebo, ViroMed’s U.S. division VM BioPharma said yesterday. (more…)
Read MoreCompression Sock for Excessive Sitting or Standing
Success as an HME compression provider takes commitment, education and an understanding that there is more to compression beyond the feet.
The compression sock is an integral product to carry for any HME provider committed to using compression technology to help patients. Compression doesn’t even need to be required due a medical condition – it’s an almost universal need. Sitting or standing for excessive amounts of time can be terrible for your health, especially the feet. For example, sitting with your legs crossed beneath your chair can cause pressure that results in swollen ankles or varicose veins. And standing all day at work can cause issues from your neck all the way to your feet. (more…)
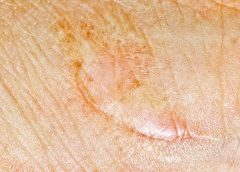
Read MoreDoctors Find New Natural Way to Prevent Scars
Scars are a particularly sore subject for most people. Not only are they aesthetically unpleasing, but some of them can prove painful. That’s why research into minimizing the appearance of scars continues to be a central priority of wound care-related research. In the last several months alone, there have been quite a few exciting such breakthroughs. (more…)
Read MoreA new way of healing wounds in the future discovered by scientists
Scientists at Ohio State University have developed a new method that has the capability of changing the body’s existing cells into new cells to promote healing. The method, called Tissue Nanotransfection (TNT), reprograms cells through a device that uses nanotechnology. The way it would work: First, doctors would apply a light electrical stimulation to the surface of the skin. They would then place a small chip about the size of a cuff link onto the site of the wound. In less than a second, this chip would deliver reprogramming factors (pre-programmed DNA or RNA) non-invasively into living skin cells via a high-intensity, focused electric field, converting them into whatever type of cells a scientist or doctor may choose. (more…)
Read More