By Matthew Steinhauser, University of Pittsburgh
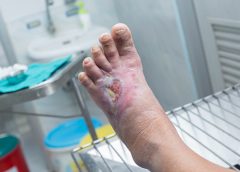
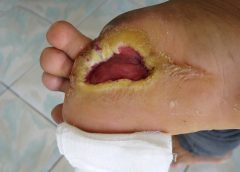
I recently visited an 83-year-old patient in the hospital after EMTs rushed her to the ER with an infected leg wound. Her ordeal started inconspicuously when she bumped into the sharp edge of a table and developed a small cut. The patient’s wound didn’t close, but she ignored it until she woke up in pain one morning two weeks after first injuring her leg. Her daughter called 911 after noticing angry, red skin discoloration and pus – both signs of an infection. Our medical team treated her with IV antibiotics and cleared up the infection, but the wound did not fully close until at least a month later, well after she was discharged from the hospital.
How different the story is when children get a cut. They may scream initially, but within days, the scab falls off, revealing new skin. Why was healing so delayed in my 83-year-old patient compared to a healthy child?
The answer is age. Decades of life slow down healing for most tissues, and wounds in skin can offer a window into why this slowdown occurs.
Three stages of wound healing
I am physician who studies how aging predisposes patients to diseases like diabetes and whether behavioral changes such as intermittent fasting may slow down aging. In order to understand why the skin wound in my older patient healed so slowly, it is important to first understand how wounds heal under the ideal conditions of youth.
The wound healing process is classically categorized into three stages.
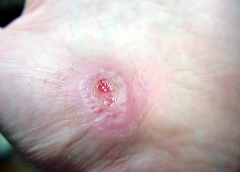
Right after a wound occurs, the inflammatory response begins.
Jpbarrass via Wikimedia Commons
The first stage is inflammation, essentially the body’s attempt to clean the wound. During the inflammatory phase, immune cells called phagocytes move into the wound, kill any contaminating bacteria, and ingest and dispose of dead cells and debris.
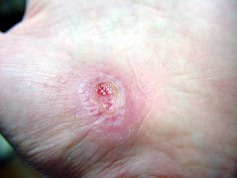
Jpbarrass via Wikimedia Commons
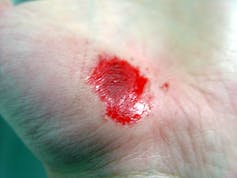
Inflammation sets the stage for the regenerative phase, where several processes work in concert to regrow damaged skin. Replacement skin cells are born when cells at the edge of the wound divide, while fibroblast cells lay down a supportive scaffolding called the extracellular matrix. This holds the new cells together. Any damaged supporting structures of the skin, such as the blood vessels that supply critical oxygen and nutrients, also need to regrow. The second stage effectively closes the wound and restores a protective barrier against bacteria.
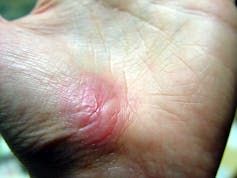
Jpbarrass via Wikimedia Commons
The regenerative phase is a relatively quick, but tenuous fix – new skin is fragile. The final remodeling phase plays out over a couple of years as the new skin is progressively strengthened by several parallel processes. The extracellular matrix, which was initially laid down in a haphazard fashion, is broken down and replaced in a more durable way. Any residual cells from prior phases that are no longer needed – such as immune cells or fibroblasts – become inactive or die. In addition to strengthening the new skin, these collective actions also account for the tendency of scars to visibly fade with time.
Products
Diseases disrupt the healing process
One major way aging can derail the orderly and efficient progression through the stages of healing is through the health problems that stem from diseases of old age.
Diabetes is one example of a disease that is strongly associated with older age. One of the many ways that diabetes negatively affects healing is by causing blood vessels to narrow. As a consequence of inadequate circulation, crucial nutrients and oxygen do not reach the wound in sufficient quantities to fuel the second regenerative phase.
Diabetes is just one of many age-related diseases that disrupts normal processes in the body such as wound healing.
Cells age too
Aside from the negative impacts of age-associated diseases, cells themselves age. In an extreme sign of aging called cellular senescence, cells permanently lose the ability to divide. Senescent cells accumulate in skin and many other organs as people age and cause a host of problems.
When cells divide more slowly – or when they stop dividing altogether due to senescence – skin becomes thinner. The replacement of fat cells, which form a cushioning layer under the skin, also declines with age. The skin of older patients is therefore more prone to injury in the first place.
Once an older person’s skin is injured, the skin has a harder time healing properly as well. Aging and senescent immune cells cannot defend against bacteria, and the risk of serious skin infection rises. Then in the regenerative stage, slow rates of cell division translate into slow skin regrowth. My patient exhibited all of these negative effects of age – her thin, almost translucent skin ruptured from a minor bump, became infected and took nearly two months to fully regrow.
But senescent cells are more than just dysfunctional bystanders. For reasons that are not yet fully understood, senescent cells release toxic byproducts that damage surrounding tissue and drive inflammation – even when there’s no bacterial threat present. Some of these byproducts can even accelerate senescence in neighboring cells. This suggests that intrinsic aging of cells is in essence contagious and senescent cells actively fuel an uncontrolled cycle of inflammation and tissue damage that further impedes successful regeneration and healing.
A whole body problem
As the most outwardly visible tissue of the body, the skin provides a window into why people heal more slowly with age, but all tissues can be injured and are susceptible to the effects of aging. Injuries may be small, repetitive and build up over time – like the effect of smoking on the lungs. Or they may be discrete and dramatic – such as the death of heart cells with a heart attack. Different tissues may heal in different ways. Yet all tissues share a sensitivity to the repercussions of an aging immune system and a decline in the ability to regrow dead or damaged cells.
Understanding why healing slows down with age is important, but my patient asked a very practical question that physicians often face in one form or another: “Doctor, what can you do for me?”
Unfortunately, current treatment of wounds is fairly old-fashioned and often ineffective. Some of the options available include wound dressing changes, antibiotics when the wound is infected or treatment in a high oxygen chamber when circulation is bad due to diabetes.
There is hope, though, that medicine can do better and that progress in understanding the aging process will lead to new therapies. Neutralizing senescent cells in mice, for example, improves a variety of age-associated diseases. While it is way too early to say that researchers have discovered the fountain of youth, I am optimistic for a future when physicians will bend the aging curve and make skin and other organs heal faster and better.![]()
Matthew Steinhauser, Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.