This issue marks the fourth anniversary of the “Best of the Best” issue of Wound Care Advisor, the official journal of the National Alliance of Wound Care and Ostomy. Fittingly, it comes during an Olympics year. Since 1904, the Olympics have awarded gold medals to athletes whose performance makes them the “best of the best.” This year, we’re proud to present our own “Best of the Best” in print format. (more…)
Read MoreSearch Results for: Wounds
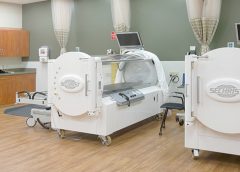
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as adjunct therapy for wound care
Why would a patient with a wound spend almost 2 hours a day, 5 days a week, in a locked chamber receiving 100% oxygen? The answer is that medical grade hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can be a valuable adjunct therapy for selected types of wounds.
In this article, I’ll focus on hospitals and clinics that follow guidelines from the Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society as I give you a brief overview of how HBOT works and its use in wound care. (more…)
2016 Journal: July – August Vol. 5 No. 4
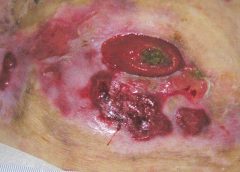
Understanding NPUAP’s updates to pressure ulcer terminology and staging
On April 13, 2016, the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) announced changes in pressure ulcer terminology and staging definitions. Providers can adapt NPUAP’s changes for their clinical practice and documentation, but it’s important to note that, as of press time, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has not adopted the changes. This means that providers can’t use NPUAP’s updates when completing CMS assessment forms, such as the Minimum Data Set (MDS) or Outcome and Assessment Information Set (OASIS). Instead, they must code the CMS assessment forms according to current CMS instructions and definitions. In addition, there is no ICD-10 code for pressure injury. (more…)
Read MorePreparing the wound bed: Basic strategies, novel methods
The goal of wound-bed preparation is to create a stable, well-vascularized environment that aids healing of chronic wounds. Without proper preparation, even the most expensive wound-care products and devices are unlikely to produce positive outcomes.
To best prepare the wound bed, you need to understand wound healing physiology and wound care basics, as well as how to evaluate the patient’s overall health and manage wounds that don’t respond to treatment. (See Normal wound healing.) (more…)
Read MoreAssessing footwear in patients with diabetes
Inappropriate footwear is the most common source of trauma in patients with diabetes. Frequent and proper assessment of appropriate footwear is essential for protecting the diabetic foot from ulceration.
Here is a step-by-step process for evaluating footwear. Be sure to evaluate footwear with the patient walking, standing, and sitting. (more…)
Read MoreClinical Notes: biofilm, bariatric surgery, statins and more
Management of biofilm recommendations
The Journal of Wound Care has published “Recommendations for the management of biofilm: a consensus document,” developed through the Italian Nursing Wound Healing Society.
The panel that created the document identified 10 interventions strongly recommended for clinical practice; however, panel members noted that, “there is a paucity of reliable, well-conducted clinical trials which have produced clear evidence related to the effects of biofilm presence.” (more…)
Read More2015 Journal: November – December Vol. 4 No. 6
2016 Journal: March – April Vol. 5 No. 2
2016 Journal: January – February Vol. 5 No. 1
Wise use of antibiotics in patients with wound infections
Antibiotic resistance is a pressing public health threat not only in the United States, but worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is one of the major threats to human health.
Despite these concerns, antibiotics continue to be widely used—and overused. In long-term care, for instance, antibiotics are the most frequently prescribed medications, with as many as 70% of residents receiving one or more courses per year. And antibiotics are consistently ordered for suspected pressure ulcer infections.
Here is what clinicians who care for patients with wounds can do to help reduce antibiotic resistance. (more…)
Read MoreUnderstanding radiation dermatitis
According to the National Cancer Institute, an estimated 1.6 million new cases of cancer will have been diagnosed in the United States in 2015. During the course of their disease, most cancer patients receive radiation therapy.
Delivering high energy in the form of waves or particles, radiation therapy alters the DNA of cancer cells, causing their death. Radiation can be administered either externally or internally (through materials placed into the body). It’s given in fraction doses, with the total recommended dose divided into daily amounts. Treatment, including the total dose, is determined on an individual basis.
Although improvements have been made in delivery of radiation therapy, approximately 95% of patients who receive it experience a skin reaction. What’s more, radiation therapy commonly is given concurrently with chemotherapy or targeted therapy to improve survival, which increases the toxicity risk. (more…)
Read More