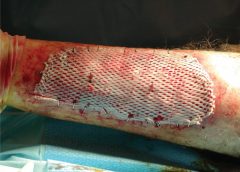
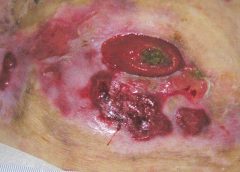
Around 6.5 million patients in the U.S. suffer from chronic wounds, such as pressure injuries or ulcers. Treatment costs $25 billion each year, representing a sizable and growing problem. Despite the wide impact of chronic wounds, it’s rare to see specialized, effective wound care delivered across the care continuum.
A chronic non-healing wound is a surrogate marker for illness. These patients require holistic management of their co-morbidities and continuity across care settings.
Despite this, a great deal of emphasis has been placed on treating wounds as singular events, managed topically with expensive dressings and support surfaces. This is only a small part of wound healing.
As a physician focused solely on wound care, I have learned that we must shift the focus from simply treating the wound to treating the wounded patient. The impact in the post-acute care setting in particular is worthy of evaluation and discussion, as up to 29% of patients in long-term care facilities will experience a pressure ulcer, posing serious legal, financial, and staffing implications.
For those providers working outside long-term care, there is little understanding of challenges facing LTC providers. Acute providers do not often ask, for example, how are my LTC partners reimbursed? How are they staffed? What are the requirements and regulatory pressures they face? Asking these questions would facilitate a more productive dialogue with a focus on collaborative prevention, rather than waiting until a chronic wound occurs in the LTC setting.
Creating an integrated wound care community
To address the needs of the present and growing population of patients with chronic wounds, Healogics developed an integrated wound care community model, to coordinate the wound healing process across all care settings. The program utilizes Healogics Specialty Physicians, a subspecialty group of physicians and providers with extensive training solely focused on wound care.
HSPs provide expert inpatient consultation and ensure safe transition of patients out of the hospital into the appropriate care setting. Because HSPs see the patient regardless of post-discharge venue, patients receive the same quality of care whether they are going home, to a skilled-nursing, assisted living, or LTC setting. Because chronic wounds are surrogate markers for illness, we have realized it’s essential to have an integrated, multi-setting, and multi-disciplinary process to treat the patient and their co-morbidities.
Data collected at a pilot IWCC site in the Midwestern U.S. from 2014 to 2016 revealed very positive trends for chronic wound patients. In the acute care setting, the average length of stay decreased from 9.41 days to 5.64 days, and total cost of care per patient was reduced from $10,670 to $7,248.
We’re excited by these promising results, which were revealed at the American College of Wound Healing and Tissue Repair Conference last December. We look forward to refining and expanding the model by helping our partners in acute and LTC settings standardize their practices, use evidence-based clinical guidelines, mobilize technologies and processes, and pay critical attention to patient safety and value-based outcomes.
When it comes to wound healing, no venue of care should operate alone—an integrated solution that creates continuity for the patient is critical. There are four things LTC facilities can do to break down the silos:
Read more at McKnight’s
Read More