- Alginate Dressing: download | 46KB
- Ankle Brachial Index: download | 50KB
- Diabetes Foot Examination: download |
- Debridement Tool: download | 125KB
- Job Task Analysis: download | 61KB
- Lanarkshire Oximetry Index: download | 172KB
- Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) – Cycle Planning Sheet: download | 60KB
- PDSA Cycle Progress Sheet: download | 58KB
- PDSA Reporting Form: download | 60KB
- SBAR wound and skin provider communication record: download | 46KB
- Weekly Skin Assessment: download | 2MB
Search Results for: skin
eBooks
Long-Term Outcome of Pediatric Traumatic Wound Repair: Suture Versus Tissue Adhesive
Summary
This project is an observational trial investigating wound cosmetic appearance after repair of traumatic skin lacerations in the head area of pediatric patients with two different approaches to skin closure: sutures versus tissue adhesive. Photographs will be taken at two follow-up visits after repair and later encryptedly assessed by external plastic surgeon using standard cosmetic assessment scales. The investigators hypothesize that cosmetic wound outcome will be equivalent in these two wound repair treatment options.
Description
Investigation of the long-term outcome of 400 pediatric patients with traumatic skin lacerations in the head area. After primary wound repair with suture or with tissue adhesive, eligible patients will be enrolled on the emergency department (baseline visit). The second follow-up visit will take place 5-10 days after the baseline visit and the third follow-up visit will be completed 6-12 months after trauma. At both follow-up visits, clinical examination and a brief interview will be performed. Foto documentation is completed at both the baseline and the follow-up visit.
Encrypted foto documentation will be evaluated by blinded external plastic surgeons. Primary Outcome is the cosmetic appearance using standard assessment scales, secondary outcomes are the occurrence of complications, cost-effectiveness and patient’s satisfaction.
Read more at BioPortfolio
Read MoreBreaking silos: Effective wound healing means treatment across the continuum
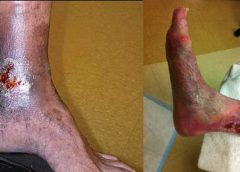
Around 6.5 million patients in the U.S. suffer from chronic wounds, such as pressure injuries or ulcers. Treatment costs $25 billion each year, representing a sizable and growing problem. Despite the wide impact of chronic wounds, it’s rare to see specialized, effective wound care delivered across the care continuum.
A chronic non-healing wound is a surrogate marker for illness. These patients require holistic management of their co-morbidities and continuity across care settings.
Despite this, a great deal of emphasis has been placed on treating wounds as singular events, managed topically with expensive dressings and support surfaces. This is only a small part of wound healing.
As a physician focused solely on wound care, I have learned that we must shift the focus from simply treating the wound to treating the wounded patient. The impact in the post-acute care setting in particular is worthy of evaluation and discussion, as up to 29% of patients in long-term care facilities will experience a pressure ulcer, posing serious legal, financial, and staffing implications.
For those providers working outside long-term care, there is little understanding of challenges facing LTC providers. Acute providers do not often ask, for example, how are my LTC partners reimbursed? How are they staffed? What are the requirements and regulatory pressures they face? Asking these questions would facilitate a more productive dialogue with a focus on collaborative prevention, rather than waiting until a chronic wound occurs in the LTC setting.
Creating an integrated wound care community
To address the needs of the present and growing population of patients with chronic wounds, Healogics developed an integrated wound care community model, to coordinate the wound healing process across all care settings. The program utilizes Healogics Specialty Physicians, a subspecialty group of physicians and providers with extensive training solely focused on wound care.
HSPs provide expert inpatient consultation and ensure safe transition of patients out of the hospital into the appropriate care setting. Because HSPs see the patient regardless of post-discharge venue, patients receive the same quality of care whether they are going home, to a skilled-nursing, assisted living, or LTC setting. Because chronic wounds are surrogate markers for illness, we have realized it’s essential to have an integrated, multi-setting, and multi-disciplinary process to treat the patient and their co-morbidities.
Data collected at a pilot IWCC site in the Midwestern U.S. from 2014 to 2016 revealed very positive trends for chronic wound patients. In the acute care setting, the average length of stay decreased from 9.41 days to 5.64 days, and total cost of care per patient was reduced from $10,670 to $7,248.
We’re excited by these promising results, which were revealed at the American College of Wound Healing and Tissue Repair Conference last December. We look forward to refining and expanding the model by helping our partners in acute and LTC settings standardize their practices, use evidence-based clinical guidelines, mobilize technologies and processes, and pay critical attention to patient safety and value-based outcomes.
When it comes to wound healing, no venue of care should operate alone—an integrated solution that creates continuity for the patient is critical. There are four things LTC facilities can do to break down the silos:
Read more at McKnight’s
Read MoreManaging chronic venous leg ulcers — what’s the latest evidence?
Chronic venous leg ulcers (CVLUs) affect nearly 2.2 million Americans annually, including an estimated 3.6% of people over the age of 65. Given that CVLU risk increases with age, the global incidence is predicted to escalate dramatically because of the growing population of older adults. Annual CVLU treatment-related costs to the U.S. healthcare system alone are upwards of $3.5 billion, which are directly related to long healing times and recurrence rates of over 50%.
CVLUs are not only challenging and costly to treat, but the associated morbidity significantly reduces quality of life. That makes it critical for clinicians to choose evidence-based treatment strategies to achieve maximum healing outcomes and minimize recurrence rates of these common debilitating conditions. These strategies, which include compression therapy, specialized dressings, topical and oral medications, and surgery, are used to reduce edema, facilitate healing, and avert recurrence. (more…)
Read MoreWelcome to WoundCareAdvisor.com
Woohoo! You’re on the WoundCareAdvisor.com list!
Now that’s over with, why not get to know us more and take a look around our site?
I want free eBooks to Advance my Career.
Wound Care Advisor eBooks are interactive digital tools full of insightful content, white papers and tutorials on trending topics that are assembled from the editorial staff along with supportive content provided by our marketing partners.
I want to watch free
Webinars to Continue my Education.
Educate yourself on various products, valuable healthcare information, or continuing your education by exploring the archive of nursing Webinars.
I want to learn more Best Practices.
Accurate and considered wound assessment is essential to fulfill professional nursing requirements and ensure appropriate patient and wound management.
Stem Cell Dynamic Therapy Could Heal Wounds
It’s necessary for the skin to heal the wounds after getting injured. For the first time, scientists discovered that the changing stem cell dynamics contribute to wound healing. The main purpose of these studies was to understand how stem cells differentiate, migrate, and proliferate to repair the tissue damage after trauma.
A team from Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) started their research on stem cells. Professor of ULB, Dr. Cédric Blanpain MD/Ph.D, WELBIO investigator and the lead researcher of this study, defined the cellular and molecular mechanisms that play active roles in wound healing. The research report was first published in the Journal of Nature Communications.
The skin of a creature is just like an outer shield which protects the inner tissues and other organs from outer injuries. If somehow the outer shield gets disrupted then body activates a cascade of cellular and molecular event to repair the damage and restore skin integrity. ScienceDaily reported that minor defects in these events lead to improper repair causing acute and chronic wound disorders.
In the new study, scientists revealed that distinct stem cells populations contribute in healing the wound. Although it is not cleared yet how proliferation, differentiation, and migration get balanced by stem cell populations during the healing process. Co-author of this study Dr.Sophie Dekoninck said in a statement,“The molecular characterization of the migrating leading edge suggests that these cells are protecting the stem cells from the infection and mechanical stress allowing a harmonious healing process”.
Read more at The Science Times
Read MoreUsing fat to help wounds heal without scars
Philadelphia – Doctors have found a way to manipulate wounds to heal as regenerated skin rather than scar tissue. The method involves transforming the most common type of cells found in wounds into fat cells – something that was previously thought to be impossible in humans. Researchers began this work at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which led to a large-scale, multi-year study in connection with the Plikus Laboratory for Developmental and Regenerative Biology at the University of California, Irvine. They published their findings online in the journal Science on Thursday, January 5th, 2017.Fat cells called adipocytes are normally found in the skin, but they’re lost when wounds heal as scars. The most common cells found in healing wounds are myofibroblasts, which were thought to only form a scar. Scar tissue also does not have any hair follicles associated with it, which is another factor that gives it an abnormal appearance from the rest of the skin. Researchers used these characteristics as the basis for their work – changing the already present myofibroblasts into fat cells that do not cause scarring. (more…)
Read MoreFrequently asked questions about support surfaces
The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) describes support surfaces as “specialized devices for pressure redistribution designed for management of tissue loads, microclimate, and/or other therapeutic functions.” These devices include specialized mattresses, mattress overlays, chair cushions, and pads used on transport stretchers, operating room (OR) tables, examination or procedure tables, and gurneys. Some support surfaces are part of an integrated bed system, which combines the bed frame and support surface into a single unit. (more…)
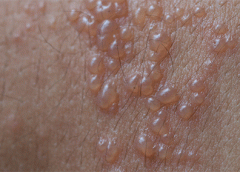
Read MoreHerpes zoster: Understanding the disease, its treatment, and prevention
Herpes zoster (HZ, also called shingles) is a painful condition that produces a maculopapular and vesicular rash. Usually, the rash appears along a single dermatome (band) around one side of the body or face.
In most cases, pain, tingling, burning, or itching occurs a few days before the rash. Next, blisters form, scabbing over in 7 to 10 days. In rare cases, the rash is widespread, resembling varicella zoster (VZ, or chickenpox) rash. Pain can range from mild to severe and may be dull, burning, or gnawing. It may last weeks, months, or even years after the blisters heal. Shingles on the face may impair vision or hearing. (more…)
Read MoreKnowing when to ask for help
As a wound care expert, you’re probably consulted for every eruption, scrape, and opening in a patient’s skin. Occasionally during a patient assessment, you may scratch your head and ask yourself, “What is this? I’ve never seen anything like it.”
Most wound care experts want to help heal everyone, and most of us love a challenge. But when should we step back and consider referring the patient to another clinician? (more…)
Read More