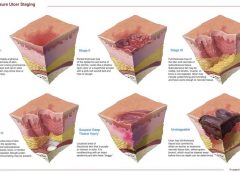
NPUAP releases new position statement on exposed cartilage as Stage IV ulcer
The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) has released a new position statement, “Pressure ulcers with exposed cartilage are Stage IV pressure ulcers,” which states that pressure ulcers with exposed cartilage should be classified as Stage IV.
NPUAP notes that although the presence of “visible or palpable cartilage at the base of a pressure ulcer” wasn’t included in Stage IV terminology, cartilage “serves the same anatomical function as bone,” so it fits into the current Stage IV definition, “Full thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon or muscle. Slough or eschar may be present on some parts of the wound bed. Often including undermining and tunneling.”
Medicare expenditures for diabetic foot care varies significantly by region
Medicare spending on patients with diabetes who have foot ulcers and lower extremity amputations varies significantly by region, according to a study in Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, but more spending doesn’t significantly reduce 1-year mortality.
“Geographic variation in Medicare spending and mortality for diabetic patients with foot ulcers and amputations” examined data from 682,887 patients with foot ulcers and 151,752 patients with lower extremity amputations.
Macrovascular complications in patients with foot ulcers were associated with higher spending, and these complications in patients with amputations were more common in regions with higher mortality rates.
Rates of hospital admission were associated with higher spending and increased mortality rates for patients with foot ulcers and amputations.
“Geographic variation in Medicare spending and mortality rates for diabetic patients with foot ulcers and amputations is associated with regional differences in the utilization of inpatient services and the prevalence of macrovascular complications,” the study concludes.
Patients who develop pressure ulcers in hospital more likely to die
Medicare patients who develop pressure ulcers in the hospital are more likely to die during the hospital stay, have longer lengths of stay, and to be readmitted within 30 days after discharge, according to a study of 51,842 patients in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
“Hospital-acquired pressure ulcers: results from the National Medicare Patient Safety Monitoring System Study” found that 4.5% of patients developed at least one new pressure ulcer during their hospitalization. Length of stay averaged 4.8 days for patients who didn’t develop a pressure ulcer, compared to 11.2 days for those with a new pressure ulcer.
Patients with diabetic foot ulcers may have higher risk of death
Patients with diabetes who have foot ulcers have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality, according to a meta-analysis in Diabetologia.
“The association of ulceration of the foot with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis” notes that the more frequent occurrence of cardiovascular disease only partly explains the increased mortality rate. Other explanations may include the more advanced stage of diabetes associated with those who had foot ulcers.
A Drugs.com article about the study reported that “analysis of data from more than 17,000 diabetes patients in eight studies found that the more than 3,000 patients with a history of foot ulcers had an extra 58 deaths per 1,000 people each year than those without foot ulcers.”
The study authors emphasize the importance of screening patients with diabetes for foot ulcers so intervention can begin early, as well as lowering cardiovascular risk factors.
Access patient information on foot care from the American Diabetes Association.
Nurse’s innovation for ostomy patients could improve quality of life
An oncology nurse in Australia has developed StomaLife, an alternative to ostomy bags.
StomaLife is a ceramic appliance that eliminates the need for an ostomy bag. According to the StomaLife website, the appliance uses a magnetic implant technology that provides a “pushing force” from within the body outward in order to keep the site intact, while a second part is placed on the stoma site. A cotton gauze pad is used between the skin and the appliance to keep the site separated and to provide air circulation to the surrounding skin.
“The benefits of StomaLife to ostomy patients are continence all day, reduced skin irritation and infection, odour and sound control, leak prevention, waste material flow control and on-demand gas release,” says Saied Sabeti.
StomaLife still needs to be tested and is not yet being produced.
View: StomaLife video
New laser-activated bio-adhesive polymer aims to replace sutures
The Journal of Visualized Experiments, a peer-reviewed video journal, has published “A chitosan based, laser activated thin film surgical adhesive, ‘SurgiLux’: preparation and demonstration.”
SurgiLux is a laser-activated, bio-adhesive polymer that is chitosan-based. Chitosan is a polymer derived from chitin, which is found in fungal cell walls or in exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects. This molecular component allows SurgiLux to form low-energy bonds between the polymer and the desired tissue when it absorbs light.
The technology may be able to replace traditional sutures in the clinical setting. SurgiLux polymer can achieve a uniform seal when activated by a laser and has antimicrobial properties, which help prevent a wound from becoming infected. It also maintains a barrier between the tissue and its surroundings.
SurgiLux has been tested both in vitro and in vivo on a variety of tissues, including nerve, intestine, dura mater, and cornea.
Palliative care raises patient satisfaction and reduces costs
Kaiser Permanente’s home-based palliative care program increased patient satisfaction and decreased emergency department visits, inpatient admissions, and costs, according to an innovation profile in the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Innovations Exchange.
“In-home palliative care allows more patients to die at home, leading to higher satisfaction and lower acute care utilization and costs” notes that the program uses an interdisciplinary team of providers to manage symptoms and pain, provide emotional and spiritual support, and educate patients and family members on an ongoing basis about changes in the patient’s condition.
Other components of the program include a 24-hour nurse call center, biweekly team meetings, and bereavement services to the family after the patient dies.
More research needed to determine efficacy of maggot debridement therapy
“The efficacy of maggot debridement therapy (MDT)—a review of comparative clinical trials” concludes that “poor quality of the data used for evaluating the efficacy of MDT highlights the need for more and better designed investigations.”
The authors of the article in International Wound Journal reviewed three randomized clinical trials and five nonrandomized clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of sterile Lucilia sericata applied on ulcers.
The studies found that MDT was “significantly more effective than hydrogel or a mixture of conventional therapy modalities, including hydrocolloid, hydrogel and saline moistened gauze,” but the designs of the study were “suboptimal.”
Use tool to select correct antimicrobial dressing
“Ensuring that the correct antimicrobial dressing is selected,” in Wounds International, emphasizes that dressing selection should be based on assessment of the microbial burden in the wound, the wound type, and the location and condition of the wound.
The article includes a checklist that may be helpful for deciding on the level of bacterial burden in a wound. The checklist is used to determine four levels of risk—colonized: at risk; localized infection; spreading infection; and systemic infection. Each level has a corresponding definition.
A table of antimicrobial dressings reviews the antimicrobial agent and dressing form, and the article ends with a case study.