By: Ronald A. Sherman, MD; Sharon Mendez, RN, CWS; and Catherine McMillan, BA
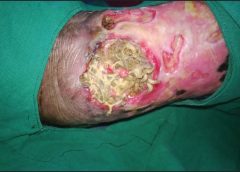
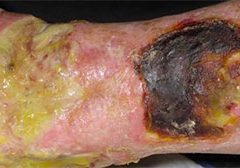
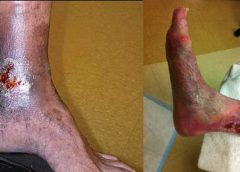
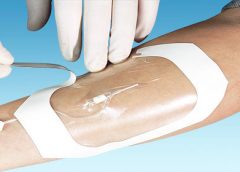
Maggot therapy is the controlled, therapeutic application of maggots to a wound. Simple to use, it provides rapid, precise, safe, and powerful debridement. Many wound care professionals don’t provide maggot therapy (also called wound myiasis) because they lack training. But having maggot therapy technology available for patients adds to your capabilities as a wound care provider. (more…)
Read More