By Beth Hoffmire Heideman, MSN, RN
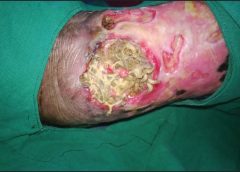
No one wants an ostomy, but sometimes it’s required to save a patient’s life. As ostomy specialists, our role is to assess and intervene for patients with a stoma or an ostomy to enhance their quality of life. We play an active role in helping patients perform self-care for their ostomy and adjust to it psychologically, starting even before surgery. (more…)
Read More