Imagine you have a health condition that affects your life every day. Then imagine being told nothing can be done about it; you’ll just have to live with it. Or worse yet, your physician tells you the problem is “you’re just fat.”
Many people with lymphedema or lipedema have no idea their condition has a name or that many other people suffer from the same thing. Although lymphedema and lipedema can’t be cured, proper management and resources can help patients cope. This article improves your grasp of these conditions, describes how to recognize and manage them, and explains how to support your patients.
To understand lymphedema and lipedema, first you need to understand how the lymphatic system functions. It makes lymph, then moves it from tissues to the bloodstream. It also plays a major role in the immune system, aiding immune defense. In addition, it helps maintain normal fluid balance by promoting fluid movement from the interstitial tissues back to the venous circulation. (See Lymphatic system: Four major functions.)
If the lymphatic system is impaired from a primary (hereditary or congenital) condition or a secondary problem, lymphedema can result. In this chronic, potentially progressive, and incurable condition, protein-rich fluid accumulates in the interstitial tissues.
Lymphedema basics
Lymphedema occurs in four stages.
Stage 0. During this stage (also called the subclinical or latency stage), transport capacity of the lymphatic system decreases but remains sufficient to manage normal lymphatic loads. Signs and symptomsaren’t evident and can be measured only by sensitive instruments, such as bioimpedance spectroscopy and optoelectronic volumetry. Without such instruments to quantify volume changes, diagnosis may rest on subjective complaints.
In this stage, limited functional reserve of the lymphatic system leads to a fragile balance between subnormal transport capacity and lymphatic loads. Added stress on the lymphatic system (as from extended heat or cold exposure, injury, or infection) may cause progression to stage 1.
Providing appropriate patient information and education, especially after surgery, can dramatically reduce the risk that lymphedema will progress to a more serious stage.
Stage 1. Considered the spontaneously reversible stage, stage 1 is marked by softtissue pliability without fibrotic changes. Pitting can be induced easily. In early stage 1, limb swelling may recede over – night. With proper management, the patient can expect the extremity to decrease to a normal size compared to that of the uninvolved limb. Otherwise, lymphedema is likely to progress to stage 2.
Stage 1 lymphedema may be hard to distinguish from edemas from other causes. Clinicians must rely on the patient history and monitor for swelling resolution with conventional management, such as compression and elevation, or note if swelling persists despite these standard interventions.
Stage 2. Sometimes called the spontaneously irreversible stage, stage 2 is identified mainly from tissue proliferation and subsequent fibrosis (called lymphostatic fibrosis). The fluid component can be removed spontaneously, but removal of the increased tissue proliferation (initially irreversible) takes more time. Tissue proliferation stems from long-standing accumulation of protein-rich fluid; over time, the tissue hardens and pitting is hard to induce. In many cases, swelling volume increases, exacerbating the already compromised local immune defense.
Consequently, infections (particularly cellulitis) are common; these, in turn, increase the volume of the affected area. Proper treatment can reduce volume.
With proper care (complete decongestive therapy [CDT]), lymphedema can stabilize during stage 2. But patients with chronic or recurrent infections are likely to progress to stage 3.
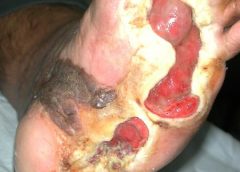
Stage 3. Also called lymphostatic elephantiasis, this stage is marked by further fluid volume increases and progression of tissue changes. Lymphostatic fibrosis becomes firmer and other skin alterations may occur, including papillomas, cysts, fistulas, hyperkeratosis, fungal infections, and ulcers. Pitting may be present. Natural skinfolds deepen (especially those of the dorsum of the wrist or ankle) and, in many cases, cellulitis recurs.
If lymphedema management starts during this stage, reduction can still occur. Even in extreme cases, with proper care and patient adherence to treatment, lymphostatic elephantiasis can be reduced so the leg is a normal or near-normal size.
Assessment and diagnosis
A thorough physical examination is the gold standard for diagnosing lymphedema. A complete patient history, body-systems review, inspection, and palpation can help determine if edema is lymphedema.
Clinically, the only test with proven reliability and validity in diagnosing lymphedema is the Stemmer sign. Fibrotic changes associated with lymphedema can lead to thickened skin over the proximal phalanges of the toes or fingers. If you can’t tent or pinch the skin on the involved extremity, lymphedema is present (a positive Stemmer sign). However, a negative finding (soft, pliable tissue) doesn’t rule out lymphedema because the condition may be in an early stage, before tissue proliferation and fibrosis have set in.
Management
Although incurable, lymphedema can be managed successfully through CDT. This approach involves proper identification of lymphedema, manual lymph drainage, skin and nail care, patient education, compression, and exercise.
CDT has two phases:
• Phase I, the intensive phase, continues until the extremity has decongested or reached a plateau. The clinician provides treatments and educates the patient about all aspects of CDT to prepare him or her for phase II. Phase I can last several weeks to several months depending on lymphedema severity.
• Phase II, the maintenance phase, begins once the extremity has decongested or plateaued. This phase still focuses on CDT, but now the patient, not the clinician, is responsible for all care. The goal is to reduce limb size while enabling the patient to become self-sufficient in managing lymphedema. Although CDT can bring significant improvements in limb size, skin quality, and function, patients must remember that phase II continues lifelong. Be sure to provide education about ongoing self-management strategies.
Lipedema: The disease they call “fat”
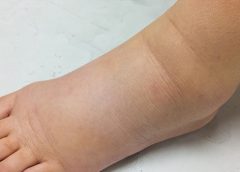
Lipedema is a painful disorder of fat deposition. Pathologic deposition of fatty tissue (usually below the waist) leads to progressive leg enlargement. Like lymphedema, lipedema is incurable but manageable. Unless managed properly, lipedema can reduce mobility, interfere with activities of daily living, and lead to secondary lymphedema. (See Lipedema stages.)
Lipedema commonly is misdiagnosed as lymphedema. However, lymphedema involves protein-rich fluid, whereas lip edema is a genetically mediated fat disorder. Because lipedema resists diet and exercise, it can lead to psychosocial complications. Lipedema occurs almost exclusively in women; typically, onset occurs between puberty and age 30. One unpublished epidemiologic study puts lip edema incidence in females at 11%. Some patients have a combination of lipedema and lymphedema. (See Viewing lipolymphedema.)
Assessment and diagnosis
As with lymphedema, lipedema diagnosis rests on clinical presentation. Lipedema characteristics include bilateral and symmetrical involvement, absence of pitting (because lipedema isn’t a fluid disorder), soft and pliable skin, and filling of the retromalleolar sulcus (called the fat pad sign.)
Key signs and symptoms include:
• feeling of heaviness in the legs (aching dysesthesia)
• easy bruising
• sensitivity to touch (called “painful fat syndrome”)
• orthostatic edema
• oatmeal-like changes to skin texture.
Nearly half of lipedema patients are overweight or obese, but many appear of normal weight from the waist up. Essentially, the upper and lower extremities don’t match. The lower extremities typically show fatty deposits extending from the iliac crest to the ankles, sparing the feet. (See Lipedema patterns.)
Management
Lipedema is best managed through weight control, as additional weight gain through adipose tissue tends to deposit in the legs. For patients with concomitant lymphedema (lipolymphedema), modified CDT helps reduce and manage lymphatic compromise. To address excess fat deposition, newer “wet” liposuction techniques have proven beneficial. These techniques gently detach adipose cells from the tissue, helping to preserve connective tissue and lymphatic vessels.
Know what to look for
In both lymphedema and lipedema, early identification and proper diagnosis are key. (See Differentiating lymphedema and lipedema.) A thorough history and physical exam will likely lead to an accurate diagnosis, if clinicians know what to look for. Proper diagnosis and treatment can prevent expensive and ineffective interventions, which can negatively affect both the patient’s condition and psychological well being.
Heather Hettrick is an associate professor at Nova Southeastern University, Department of Physical Therapy in Fort Lauderdale, Florida.
Selected references
Fat Disorders Research Society. Lipedema description.
Fife CE, Maus EA, Carter MJ. Lipedema: a frequently misdiagnosed and misunderstood fatty deposition syndrome. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2010;23(2):81-92
Herbst KL. Rare adipose disorders (RADS) masquerading as obesity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33(2):155-72.
Lipedema Project.
National Lymphedema Network. Position papers.
Schmeller W, Hueppe M, Meier-Vollrath I. Tumescent liposuction in lipoedema yields good long-term results. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166(1):161-8.
Zuther J. A closer look at lipedema and the effects on the lymphatic system. December 13, 2012. lymphedemablog.com/2012/12/13/a-closer-look-at-lipedema-and-the-effects-on-the-lymphatic-system/
Zuther J. Stages of lymphedema. October 3, 2012.
Read More