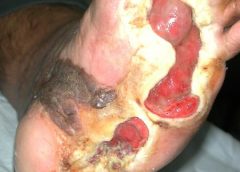
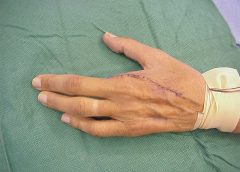
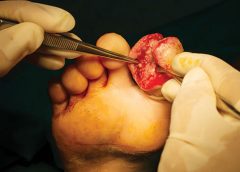
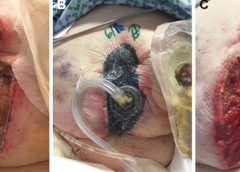
One of many dreaded tags from a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Survey is F-Tag 314 — Pressure ulcers.
CMS writes, “Each resident must receive and the facility must provide the necessary care and services to attain or maintain the highest practicable physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being, in accordance with the comprehensive assessment and plan of care.” (more…)
Read More