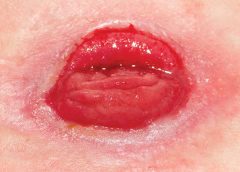
Posted: November 21, 2013
Hospital pressure-ulcer comparison data not accurate Performance scores for rates of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers might not be appropriate for comparing hospitals, according to a study in the Annals of Internal Medicine. “Hospital report cards for hospital-acquired pressure ulcers: How good are the grades?,” funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, analyzed 2 million all-payer administrative records from 448…
Posted: November 21, 2013
A variety of resources to end the year and take you into 2014. On the road again Give your patients with an ostomy this information from the Transportation Security Administration to help them navigate airport screening: • You can be screened without having to empty or expose your ostomy, but you need to let the officer conducting the screening know…
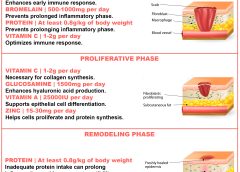
Posted: November 19, 2013
By Nancy Collins, PhD, RD, LD/N, FAPWCA, and Allison Schnitzer Nutrition is a critical factor in the wound healing process, with adequate protein intake essential to the successful healing of a wound. Patients with both chronic and acute wounds, such as postsurgical wounds or pressure ulcers, require an increased amount of protein to ensure complete and timely healing of their…

Posted: November 21, 2013
By Jeri Lundgren, BSN, RN, PHN, CWS, CWCN A pressure ulcer that a patient acquires in your facility or a patient’s existing pressure ulcer that worsens puts your organization at risk for regulatory citations as well as litigation. Unless you can prove the pressure ulcer was unavoidable, you could find yourself burdened with citations or fines, or could even end…

Posted: November 21, 2013
By Kathleen D. Pagana, PhD, RN Are you making connections that benefit your career? Are you comfortable starting a conversation at a networking session? Do you know how to exit a conversation gracefully when it’s time to move on? These are questions and concerns many clinicians share. Career success takes more than clinical expertise, management savvy, and leadership skills. Networking…

Posted: November 21, 2013
By Connie Johnson, BSN, RN, WCC, LLE, OMS, DAPWCA No matter where you work or who your distributors are, ensuring the patient has sufficient ostomy supplies can be a challenge. Whether you’re the nurse, the physician, the patient, or the family, not having supplies for treatments can heighten frustration with an already challenging situation, such as a new ostomy. Here’s…
Posted: November 21, 2013
by Donna Sardina, RN, MHA, WCC, CWCMS, DWC, OMS With uncertainty over how the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ultimately will affect operations, hospitals and other healthcare facilities are tightening up. In many areas, they’re laying off staff. In May, the healthcare industry lost 9,000 jobs—the worst month for the industry in a decade—and another 4,000 jobs were lost in July.…
Posted: November 21, 2013
Dermatologic difficulties: Skin problems in patients with chronic venous insufficiency and phlebolymphedema By Nancy Chatham, RN, MSN, ANP-BC, CWOCN, CWS; Lori Thomas, MS, OTR/L, CLT-LANA; and Michael Molyneaux, MD Skin problems associated with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and phlebolymphedema are common and often difficult to treat. The CVI cycle of skin and soft tissue injury from chronic disease processes can…
Posted: November 21, 2013
By Robyn Bjork, MPT, WCC, CWS, CLT-LANA Margery Smith, age 82, arrives at your wound clinic for treatment of a shallow, painful ulcer on the lateral aspect of her right lower leg. On examination, you notice weeping and redness of both lower legs, 3+ pitting edema, several blisters, and considerable denudement of the periwound skin. She is wearing tennis shoes…
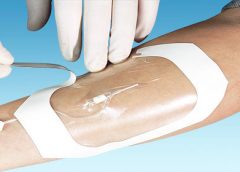
Posted: November 21, 2013
By Nancy Morgan, RN, BSN, MBA, WOC, WCC, DWC, OMS Each issue, Apple Bites brings you a tool you can apply in your daily practice. Description Hydrated polymer (hydrogel) dressings, originally developed in the 1950s, contain 90% water in a gel base, which helps regulate fluid exchange from the wound surface. Hydrogel dressing are usually clear or translucent and vary…