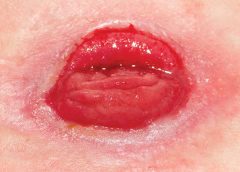
Imagine watching your skin tear, bleed, and turn purple. Imagine, too, the pain and disfigurement you’d feel.
What if you had to live through this experience repeatedly? That’s what many elderly people go through, suffering with skin tears through no fault of their own. Some go on to develop complications.
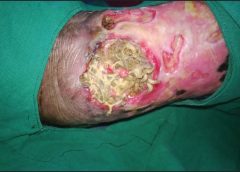
A skin tear is a traumatic wound caused by shear, friction, or blunt-force trauma that results in a partial

Buzz Report: Latest trends, part 2
Keeping clinicians up-to-date on clinical knowledge is one of the main goals of the Wild on Wounds (WOW) conference held each September in Las Vegas. Every year, I present the opening session, called “The Buzz Report,” which focuses on the latest-breaking wound care news—what’s new, what’s now, and what’s coming up. I discuss new products, practice guidelines, resources, and tools from the last 12 months in skin, wound, and ostomy management. In…

Caution: Checklists may lead to inaccurate documentation
Using a checklist form to document wound care can make the task easier and faster—and help ensure that you’ve captured all pertinent data needed for assessment, reimbursement, and legal support. But the form itself may not be comprehensive; some important fields may be missing. Recently, we at Wound Care Advisor received a question from a clinician who was having trouble deciding how to code a patient’s wound in her hospital’s…
Clinical Notes: ostomy, pressure ulcer, burn treatment
Self-management ostomy program improves HRQOL A five-session ostomy self-care program with a curriculum based on the Chronic Care Model can improve health-related quality of life (HRQOL), according to a study in Psycho-Oncology. “A chronic care ostomy self-management program for cancer survivors” describes results from a longitudinal pilot study of 38 people. Participants reported sustained improvements in patient activation, self-efficacy, total HRQOL, and physical and social well-being. Most patients had a history of…

Clinician Resources: human trafficking, npuap, caregiver, ostomy, HIV
Check out the following resources, all designed to help you in your clinical practice. Human trafficking resources Victims of human trafficking often suffer tremendous physical and psychological damage. Clinicians play an important role in identifying potential victims so they can obtain help. Here are some resources to learn more about human trafficking. • “Addressing human trafficking in the health care setting” is an online course that includes a…

Comprehensive turning programs can avoid a pain in the back
Turning programs are essential to prevent and promote healing of pressure ulcers and to prevent the many negative effects of immobility, ranging from constipation to respiratory infections. However, turning a patient often puts a caregiver’s body in an awkward position, which can lead to musculoskeletal damage, especially back injuries. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, healthcare workers suffer…

Exercise your right to be fit!
Nearly all clinicians know exercise is good for our physical and mental health. But incorporating it into our busy lives can be a challenge. The only types of exercise some clinicians have time for are working long shifts, juggling life’s demands, balancing the books, jumping on the bandwagon, climbing the ladder of success, and skipping meals. Clinicians are in a…

FAQs about support surfaces
Support surfaces are consistently recommended for the prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers. So patients can derive optimal benefits from support surfaces, clinicians must understand how to use them effectively. This article answers several questions about these useful tools.

How to apply silver nitrate
Topical application of silver nitrate is often used in wound care to help remove and debride hypergranulation tissue or calloused rolled edges in wounds or ulcerations. It’s also an effective agent to cauterize bleeding in wounds. Silver nitrate is a highly caustic material, so it must be used with caution to prevent damage to healthy tissues.
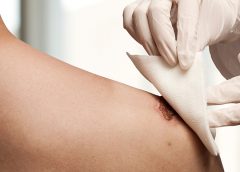
No more skin tears
Imagine watching your skin tear, bleed, and turn purple. Imagine, too, the pain and disfigurement you’d feel. What if you had to live through this experience repeatedly? That’s what many elderly people go through, suffering with skin tears through no fault of their own. Some go on to develop complications. A skin tear is a traumatic wound caused by shear, friction, or blunt-force trauma that results in a partial-…

Nutritional considerations in patients with pressure ulcers
Optimizing nutritional status is a key strategy both in preventing and managing pressure ulcers. In patients across all care settings, compromised nutrition— as from poor intake, undesired weight loss, and malnutrition—increases the risk of pressure ulcers. It contributes to altered immune function, impaired collagen synthesis, and decreased tensile strength. In many cases, malnutrition also contributes to wound chronicity and increases the risk for delayed and impaired wound healing. In patients with chronic…