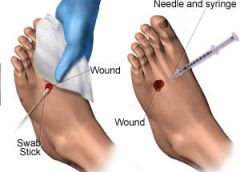
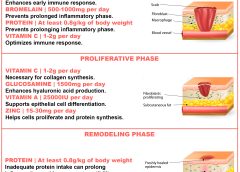
Greet the new year by tapping into some new resources.
Free app for patients with Crohn’s Disease
GI Buddy is a free tool from the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation of America that patients can use to stay on top of managing their Crohn’s Disease or ulcerative colitis symptoms. Patients can record what they eat, track their treatment and well-being, and access detailed reports. Patients also can access a video of tips for using GI Buddy, which is available online and as an iPhone app. (more…)
Read More