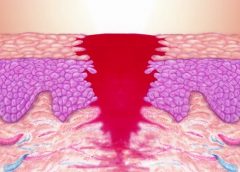
It’s necessary for the skin to heal the wounds after getting injured. For the first time, scientists discovered that the changing stem cell dynamics contribute to wound healing. The main purpose of these studies was to understand how stem cells differentiate, migrate, and proliferate to repair the tissue damage after trauma.
A team from Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) started their research on stem cells. Professor of ULB, Dr. Cédric Blanpain MD/Ph.D, WELBIO investigator and the lead researcher of this study, defined the cellular and molecular mechanisms that play active roles in wound healing. The research report was first published in the Journal of Nature Communications.
The skin of a creature is just like an outer shield which protects the inner tissues and other organs from outer injuries. If somehow the outer shield gets disrupted then body activates a cascade of cellular and molecular event to repair the damage and restore skin integrity. ScienceDaily reported that minor defects in these events lead to improper repair causing acute and chronic wound disorders.
In the new study, scientists revealed that distinct stem cells populations contribute in healing the wound. Although it is not cleared yet how proliferation, differentiation, and migration get balanced by stem cell populations during the healing process. Co-author of this study Dr.Sophie Dekoninck said in a statement,“The molecular characterization of the migrating leading edge suggests that these cells are protecting the stem cells from the infection and mechanical stress allowing a harmonious healing process”.
Read more at The Science Times
Read More