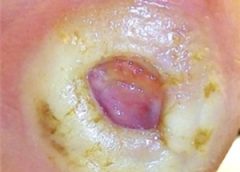
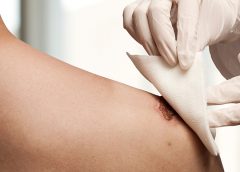
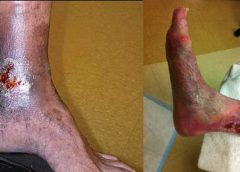
At a time when governments are under pressure to reduce healthcare costs, the global advanced wound care market is growing, driven by an aging population and rising incidences of chronic wounds.
Advanced wound care products are typically used to manage complex wounds, including burns, chronic wounds and complex trauma and surgical wounds. Chronic and complex wounds represent one of the predominant challenges to global healthcare systems because they are hard to heal and expensive to treat. (more…)
Read More